Calculate the resistance:
For Calculate the resistance Rx, a tapping key K is held down momentarily and the bridge is balanced through adjusting R3 to get no deflection in galvanometer under these conditions.
Within the bridge the total current is divided within two paths: i1 through R1 and R3, and i2 through R2 and Rx. Under the balancing conditions, the potential at points B and D must be the similar, that is the ohmic voltage drop through the resistors R1 and R2 must be the same. Therefore, the potential at B (EB) must be equal to potential at D (ED).
EB = ED ... (1)
Or i1 R1 = i2R2 ... (2)
Similarly, i1 R3 = i2 Rx ... (3)
Dividing Equation (2) through Equation (3), we get
R1 / R3 = R2/ RX
and Rx = R2 R3/R1 ... (4)
Thus, we could calculate Rx as R1, R2 and R3 are all known. The Conductance G, being the reciprocal of resistance will be,
G = R1/R2 R3 ... (5)
the input potential, Ei, is balanced by the current from amplifier output which passes through a feedback resistor (Rf). The output potential, E0 is in terms of resistance:
E0 = Ei (Rf/Rx + 1)
here Rx is the resistance of conductometric cell.
With the respect to the solution conductance, G, above equation becomes
E0 = Ei(RfG + 1)
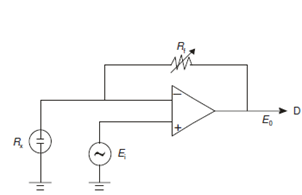
Figure: An operational amplifier control circuit for conductometric measurement.
Here Rx is the solution resistance and Rf is the feedback resistance