Color wheel:
Since these filters work through absorbing part of the radiation incident on them therefore they do not gives monochromatic light. In sequence to get a narrow band of wavelengths we could use certain filters that actually contain two glass filters; one filter absorbs strongly above a certain wavelength, while the second absorb strongly below a certain wavelength.
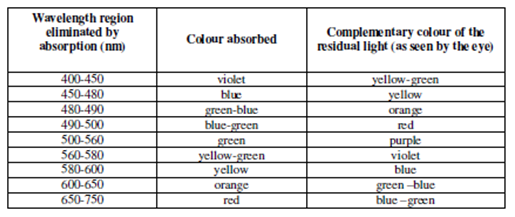
In sequence to search the color of the filter to be used us can take the help of color wheel shown in Figure, or consult a table of complementary colors given in Table.
In a color wheel, the colors, which face one another, are said to be complementary to each other. In order to measure a red colored solution, its complementary, that is, a green colored filter should be used. In the color wheel P, S and T refer to the primary, secondary and tertiary colors, respectively.
Table: Complementary Colours Chart
Absorption filters are simple and are totally adequate for several applications in visible range. Thus, for extended ranges we required interference filters. The interference filters cover a huger range than the absorption filters. Interference filters are fundamentally composed of two transparent parallel films of silver that are so close as to generate interference effects. Like interference filters are available for ultraviolet, visible and near- infrared region. The performance features of interference filters are significantly superior to those of absorption (coloured) filters. The effective bandwidths of these filters are narrower than absorption filters.