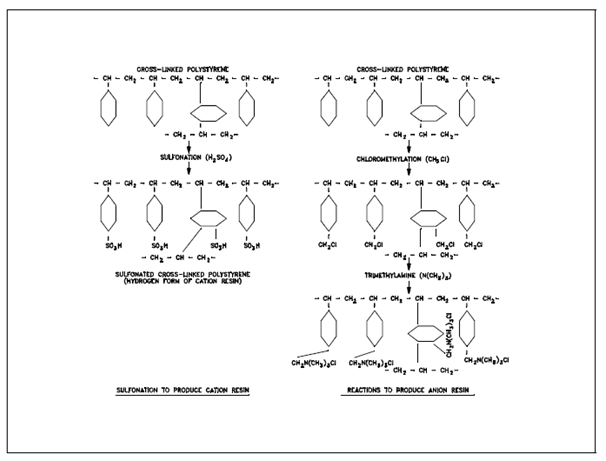
Cross-Linked Polystyrene Ion Exchange Resins:
A particular resin might be prepared in various forms according to the identity of the exchangeable ion attached. It is commonly named according to the ion present on the active sites. For instance, the resin represented through R-Cl is said to be the chloride form of the anion resin, or easily the chloride form resin. Other general forms are the hydroxyl form (R-OH), ammonium form (NH4-R), lithium form (Li-R), and hydrogen form (H-R).
The mechanics of the ion exchange procedure are somewhat complicated, other than the necessary characteristic could be understood on the basis of equilibrium concepts and recognition in which the strength of the ionic bond among the resin and an ion varies along with the particular ion. That is, for a particular resin, variant ions experience different attractions to the resin. The term affinity is frequent used to elaborate the attraction among a resin and a given ion. This affinity could be defined quantitatively through experimental determination of a parameter known as the associative affinity coefficient. To a qualitative discussion, it suffices to remember the associative affinities among a resin and different ions.