Decentralization Theorem:
The welfare gains from decentralization are often considered by reference to those deadweight losses that result from centralization. Assume that the population of a particular nation-state is divided into two distinct localities. A local public good is to be provided in each locality and the cost is to be shared equally by residents. In Fig. we illustrate the demand for the local public good of two 'representative' individuals, one from each locality. DA represents the demand of individuals in locality A and DB represents the demand of individuals in B. The marginal costs of providing this particular public good G are assumed to be constant. The price each individual is asked to pay is shown as P in the diagram. (This would be each individual's share of the marginal cost MC).
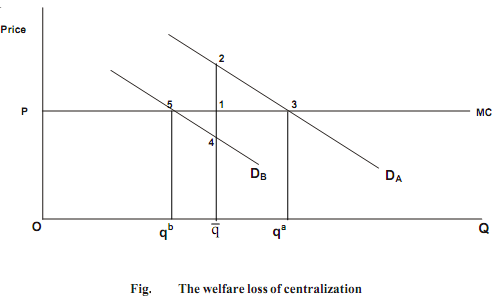
In this diagram, if a centralized regime provided a single uniform level of the good, the level of output provided could be shown as a compromise between the demands of the individuals in each locality, i.e. a level of Oq . Such a quantity is lower than the amount that would be demanded by the representative individual A, but more than that would be demanded by the representative individual B. Inevitably, welfare losses are experienced by each of these two individuals. The losses are shown as triangles 123 and 145. Triangle 123 indicates the loss that arises because individual A does not consume as much as she would choose if there were no need to compromise. She would gladly pay the amount equivalent to the area 23qa for theadditional units qa, but these would cost only (area) 13qa to be made available.
Triangle 145 indicates the welfare losses that are experienced by individual B because he is consuming more than he would otherwise choose. He pays the amount expressed by the area qb51 for the additional units qb but he values them at only qb54q.
If each area could provide itself with just the quantity of the good that it requires, these deadweight losses could be avoided. Decentralization permits each locality to provide itself with the quantity of the good it prefers. This illustrates the 'decentralization theorem'.
There are, however, a number of points to add.
1) In Fig, if qa and qb were close, then would provide a close approximation. It is evident that the greater the difference in tastes and preferences, the greater the welfare losses. Welfare losses from centralized provision increase with heterogeneity.
2) As in other cases, the deadweight welfare loss depends on the price elasticity of demand. The more inelastic the demand curves (the steeper the demand curves at points 5 and 3 in Fig.), the larger will be area of the shaded triangle. The sizes of the triangles are the key to the losses from centralization.
3) In the above analysis, if there are economies of scale in the production of the good, this will influence the optimum size of the locality. Other things being equal, there will be greater case for taking advantage of the lower average costs of larger communities.