Voltage Division Rule:
Since in series circuit, shown in Figure, current is illustrated by equation
I = V /Req
then
V1 = IR1 = V. (R1/Req)
V2 = IR2 = V. (R2 /Req)
V3 = IR3 = V. (R3 /Req)
Figure shows the resistance connected is parallel.
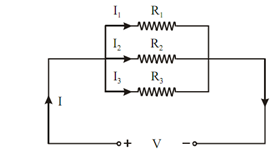
Figure: Parallel Resistors
In parallel circuits, current is divided whereas the voltage remains same across all parallel branches.
1 /Req = (1 / R1 )+ (1 / R2) + (1/ R3)
= (R2 R3 + R1 R3 + R1 R2 )/ R1 R2 R3
∴ Req = R1 R2 R3 / (R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1)
It is better to represent the circuit in conductance form.
i.e. Geq = G1 + G2 + G3