The Ideal Reheat Rankine Cycle
By increasing the steam pressure at inlet to turbine and reducing the steam pressure at exhaust will raise the thermal efficiency of Vapor Power cycle. In this system the moisture trouble will be encountered at the final phase of the turbine. To overcome this trouble the ideal reheat and Regenerative cycle process will be employed. In practice reheat and regeneration both are employed for improve the total efficiency of the vapor power cycles.
The reheat Rankine cycle is as shown in figure below. In this cycle extra low pressure turbine is added. In reheat Rankine cycle; the steam that is collected from the HP turbine is reheated with the aid of fine gases in the boiler furnace. Then the reheated steam is sent to the LP turbine and the regular power cycle. The two turbines are employed here since reheating is completed at higher pressures only. The reheating can be completed two or more phases, that will be established by economical consideration.
Advantages of Reheat Cycles:
• Reheated steam removed the erosion and corrosion to the blades of the turbine,
• Turbine output will be raised,
• ηth will be raised,
• Final dryness fraction is enhanced,
• Nozzle and blade efficiencies raised, and
• Specific steam utilization is reduced.
Efficiency Computation of Reheat Cycle:
The net heat added per kg of steam
Q = (h1 – h5) + (h3 – h2) – wP kJ/kg
Work done = W = (h1 – h2) + (h3 – h4) – wP kJ/kg
Here, wP = Pump work = h6 – h5
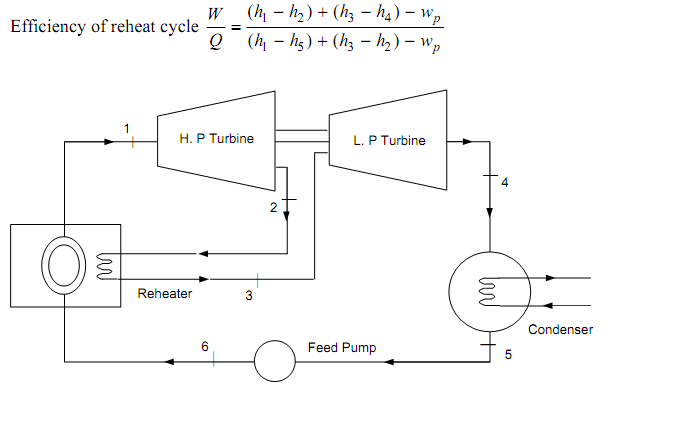
Figure: Reheat Cycle Equipment
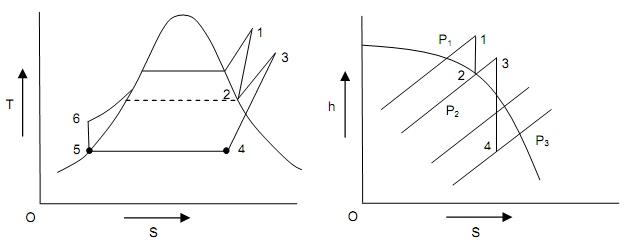
Figure: Reheat Cycle
Example:
A Rankine cycle operates among pressures of 80 bar & 0.1 bar. The maximum cycle temperature is 600oC. When the steam turbine and condensate pump efficiencies are 0.9 and 0.8, correspondingly, compute the specific work and thermal efficiency. Relevant steam table extract is specified below:
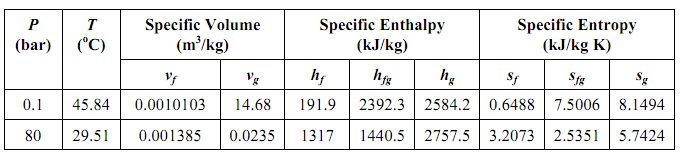
Table: 80 bar, 600oC super heat table
V = 0.486 m3/kg
h = 3642 kJ/kg
s = 7.0206 kJ/kg
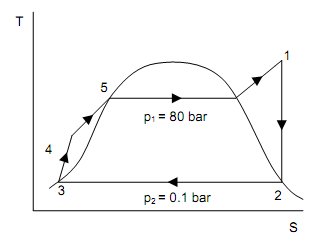
Solution:
Refer to the above figure,
At 80 bar, 600oC
h1 = 3642 kJ/kg
s1 = 7.0206 kJ/kg
Since s1 = s2
∴ 7.0206 = sf2 + x2sfg2
= 0.6488 + x2 x 7.5006
- x2 = (7.0206 - 0.6488) / 7.5006 = 0.85
Now, h2 = hf2 + x2 sfg2
- = 191.9 + 0.85 x 2392.3 = 2225.36 kJ/kg
Actual turbine work = ηturbine x (h1 – h2)
= 0.9 x (3642 - 2225.36) = 1275 kJ/kg
Pump work = vf(p2) (p1 – p2)
= 0.0010103 x (80 - 0.1) x (105 / 103) = 8.072 kJ/kg
Actual pump work = 8.072/ ηpump = 8.072/0.8 = 10.09 kJ/kg
Specific work (Wnet) = 1275 – 10.09 = 1264.91 kJ/kg
Thermal efficiency = Wnet / Q1
=> Q1 = h1 - hf4
hf4 = hf3 + Pump work
= 191.9 + 10.09 = 202 kJ
∴ Thermal efficiency ηth = 1264.91/ (3642 – 202) = 0.368 or 36.8%