Electric Solenoid Actuators:
A classical electric solenoid actuator is displays in Figure. That consists of a coil, spring, armature, and stem.
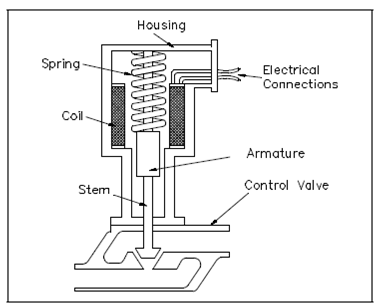
Figure: Electric Solenoid Actuator
The coil is linked to an external current supply. A spring rests on the armature to force it downward. The armature moves vertically within the coil and transmits its motion by the stem to the valve.
While current flows by the coil, a magnetic field forms around the coil. A magnetic field attracts the armature toward the middle of the coil. As the armature moves upward, the spring collapses and the valve opens. While the circuit is opened and current stops flowing to the coil, the magnetic field collapses. This permits the spring to expand and shut the valve.
A main benefit of solenoid actuators is their quick operation. Also, they are much simpler to install than hydraulic or pneumatic actuators. Therefore, solenoid actuators have two drawbacks. First one, they have only two positions: fully open and fully closed. Second one, they don't generates much force, so they commonly only operate associatively small valves.