Electrode system for measuring pH:
Therefore, the boundary potential is a measurement of the hydrogen ion activity or the pH of the external solution. To measuring pH along with glass electrode the arrangement shown in Figure are generally employed. This arrangement has glass electrode along with Ag/AgCl internal reference electrode and external reference electrode like as saturated calomel electrode (SCE). For such arrangement complete cell might be represented as:
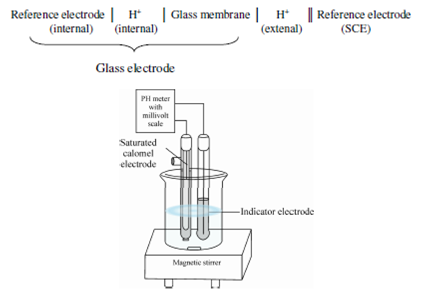
Figure: A typical electrode system for measuring pH
The cell potential is expressed as
Ecell = (E ind ) - ESCE + Ej
where ESCE is the potential because of external reference electrode, Ej is liquid-junction potential, and E ind is electrode potential of the glass electrode, which is actually a combination of three components: (i) the boundary potential, Eb, (ii) the potential of the internal Ag/AgCl reference electrode, and (iii) the asymmetry potential, Easy.
From Eq., substitute the value of Eb.
Thus, Ecell = (Eb + EAg/AgCl + Easy) - ESCE + Ej
Alternate the value of Eb in this equation
Ecell = (K1 + 0.0591 log a1 + EAg/AgCl + Easy) - ESCE + Ej
or Ecell = E* + 0.0592 log a1 = E* - 0.0591 pH
where E* is a constant, it includes all the constants and near constant source of potentials, i.e. potential of both reference electrodes, liquid-junction potential between the external reference electrode and the solution, asymmetry potential and internal boundary potential.