Nucleophilic and electrophilic unsaturated centers:
The carbonyl group of α, β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones contains nucleophilic oxygen and an electrophilic carbon. Though, α, β- aldehydes and ketones as well have another electrophilic carbon - the β-carbon. This is because of the effect of the electronegative oxygen that can result in the resonance displayed in figure. Because two electrophilic centers are present, there are two places in which a nucleophile can react.
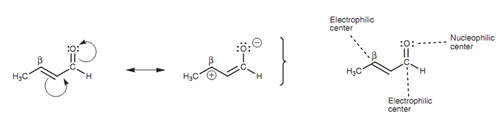
Figure: Nucleophilic and electrophilic centers.
In both of the situations, an addition reaction occurs. If the nucleophile reacts along with the carbonyl carbon, this is a general nucleophilic addition to an aldehyde or ketone and is termed as a 1, 2-nucleophilic addition. If the nucleophile adds to the β-carbon, this is termed as a 1,4- nucleophilic addition or a conjugate addition.