1, 4-Addition:
The mechanism for 1, 4- Addition includes two stages. In the 1st stage, the nucleophile employs a lone pair of electrons to make a bond to the β-carbon. At similar time, the C=C π bond breaks and both electrons are employed to make a new π bond to the carbonyl carbon. In turn this forces the carbonyl π bond to break with both of the electrons included moving onto the oxygen like a third lone pair of electrons. The resultant intermediate is an enolate ion. Now the aqueous acid is added to the reaction mixture. The carbonyl π bond is again formed that forces open the C=C π bond. These electrons are now employed to make an σ bond to a proton at α carbon.
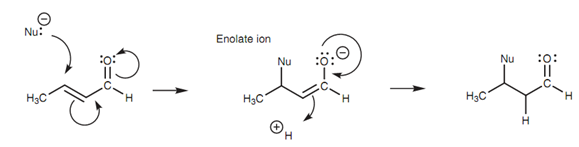
Figure: Mechanism of 1,4-nucleophilic addition.
Conjugate addition reactions can be performed with amines, or a cyanide ion. Alkyl groups can as well be added to the β-position via using organocuprate reagents. A large range of organocuprate reagents can be ready allowing the addition of primary, secondary and tertiary aryl groups, alkyl groups, and alkenyl groups.
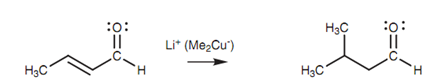
Figure: Alkylation with organocuprate reagents.