The Second:
The SI unit of time is second, represented by the lowercase non-italicized English letter s (or many times abbreviated as sec). It was defined initially as 1/60 of a minute that is 1/60 of an hour that in turn is 1/24 of a mean solar day. A second was therefore thought of as 1/86,400 of a mean solar day, and this is yet an outstanding definition as shown in figure below. Though, formally, nowadays, 1 s is defined as the quantity of time taken for a certain cesium atom to oscillate through 9.192631770 x 109 complete cycles.
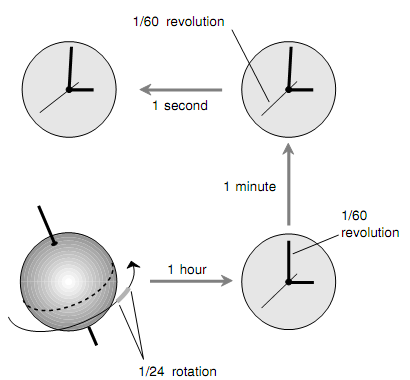
Figure: Initially, the second was defined as (1/60)(1/60)(1/24), or 1/86,400, of a mean solar day.
One second also occurs to be the time it takes for a ray of light to travel 2.99792458 x 108 m via space. This is around three-quarters of the way to the Moon. You might have listened to of the Moon being a little more than one light-second away from Earth. If you are old adequate to remember the conversations Earth-based personnel carry on with Apollo astronauts as the astronauts walked around on the Moon, you will remember the delay among comments or questions from earthlings and the replies from the moonwalkers. The astronauts were not uncertain; it took more than 2 seconds for radio signals to make a round trip between Earth and the Moon. In a certain way of thinking, time is a manifestation or expression of linear dimension, and vice-versa. Both of these features of nature are closely related by the speed of light, that Albert Einstein hypothesized is an absolute.