Constants:
Constants are the characteristics of mathematical and physical world which can be "taken for granted." They don't modify, at least not within a normal human lifetime, unless certain other factors modify too.
MATH VERSUS PHYSICS
In pure mathematics, constants are generally represented all by themselves as plain numbers without any units related. These are known as dimensionless constants and involve π the circumference-to-diameter ratio of a circle, e the natural logarithm base. In physics, there is about always a unit equivalent attached to a constant. An illustration is c, the speed of light in free space, stated in meters per second.
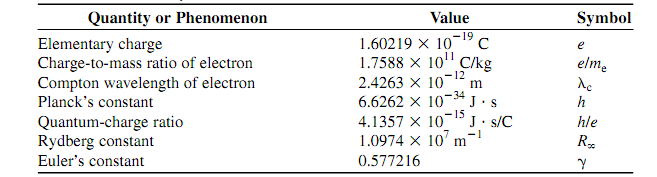
The table shown below is a list of constants you will encounter in physics. This is by no means an entire list. Do you not know that most of the constants in this table mean? Are they unknown or even arcane to you? Don't be anxious about this now. As you keep on reading this book, you will learn around many of them. This table can serve as a reference long after you are completed with this course.
Here are a few illustrations of constants from the table and how they associate to the physical universe and the physicist's modes of notion.