Nitrogen fixation
Assimilation of nitrogen in microbes is very variable. Only one group can utilize atmospheric nitrogen in a procedure called nitrogen fixation. This reaction is only seen in Proteobacteria like as Azotobacter or Rhizobium as well as in Gram-positive Bacteria such as some species of Clostridium.
Nitrogen fixation is mediated by an oxygen-sensitive enzyme called nitrogenase
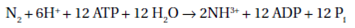
Nitrogenase plays a pivotal role in the global nitrogen cycle. This reaction is an extremely energy expensive one and is carried out anaerobically. However most nitrogen fixers are aerobes so a variety of simple differentiation methods are used to create anaerobic compartments. The heterocysts of filamentous Cyanobacteria are found in normal chains of aerobic cells, but are the main sites of nitrogen fixation. Azotobacter uses high rates of partly uncoupled aerobic metabolism for high turnover of oxygen near the cell wall. This allows the cytoplasm to become slightly anaerobic and so nitrogen fixation can occur.