Declarative and procedural memory
Learning will be occurs in various variety of distinct condition, differing in time course, stimulus requirements, and outcomes, so is classified in various ways to reflect these features in Figure. A major difference is among procedural and declarative memory.Declarative (explicit) memory is memory for facts. Declarative learning is fast; it needs few trials, requires conscious recall and may be readily forgotten. It has two parts which are dissociable in patients with cortical damage. Episodic (recollection) memories is memory for specific events, in that relation are developed at a exact time and place example for going to a gamelan concert whilst on holiday on Bali.
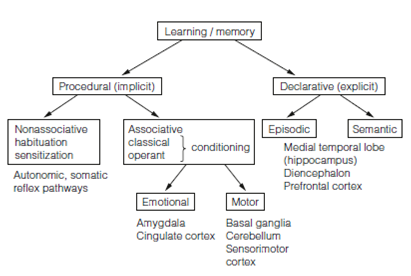
Figure: Types of memory. Structures responsible for a particular category are shown beneath. Episodic learning is also associative.
The ability of rats to navigate through a maze in which they must learn to associate their positions in the maze with cues in their surroundings, spatial navigation learning, is an extensively studied example of episodic learning. The different components of an episodic memory are distributed across disparate regions of the brain and must be bound together for recall of the episode. The extensive connections of the medial temporal lobe allow it to act as a convergence zone for the different information streams.
The second component is semantic (familiarity) memory which is memory of facts unrelated to events; that Bali is an Indonesian island can be recalled without ever having been there, so semantic memory about “knows that.” Studies of brain-damaged patients show that semantic memories are sorted into categories (sets of related objects), that appear to be stored in various areas of brain. Recall of specific items seems to need activation of multiple brain sites each of which codes for a given attribute (e.g., color, function, and name) of the item.
Procedural (motor) memory is memory for skills like as learning to swim, walk, ride a bike, or play a musical instrument. It is called knowing how memory. Procedural memory is slow it required several trials in other words; a lot of rehearsal and it is incremental in which improvement occurs gradually over time. The Performance of procedural tasks does not include conscious recall. For this reason procedural memory such as emotional memory is define as implicit memory. Once developed, procedural memories are not forgotten even after several years without rehearsal.Several tasks have both factual and skill memory parts. Playing the flute needs declarative memory for the musical notation of the procedural and score memory for the sequence of finger movements and the breathing pattern required to create the sounds.