Shunt-Wound Motor Operation:
The speed-torque relationship for a classical shunt-wound motor is display in Figure.
A shunt-wound DC motor has a decreasing torque whenever speed increases. A decreasing torque- vs-speed is caused through the armature resistance voltage drop and armature reaction. On a value of speed near 2.5 times rated speed, armature reaction becomes excessive and causing a rapid decrease in field flux and a rapid decline in torque until a stall condition is reached.
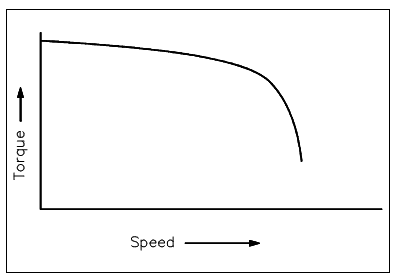
Figure: Torque-vs-Speed for a Shunt-Wound DC Motor