Positive Displacement Pump
In positive displacement pump, liquid is sucked in and then actually pushed or displaced due to the thrust exerted on it by a moving member, resulting in the lifting of the liquid to a higher elevation. The displacement of liquid can be brought about either by
• Rotary movement, and
• The displacing mechanism of Reciprocating movement.
Rotary movement is obtained in rotary pumps by using two cams or gears as shown in Figure. In this type of pump, two meshed gear rotate in opposite directions within the casing, the flow of water being around the outside of the gears with backflow prevented where the gears are meshed together giving direct displacement with smooth and non-pulsating flow. However, some internal contact of rotating parts is inevitable which cause a minor turbulence. Rotary pumps are usually used for liquids, such as, oils with good lubricating properties which cause a minor turbulence.
Reciprocating Pump, in its simple form, has a cylinder into which a piston moves to alternately suck and push water (Figure 16). Flow rate of water in such pumps almost wholly depends on the speed of the pump. Forward and backward motion of the piston is brought about by a prime mover like an electric motor, a steam engine or an oil engine.
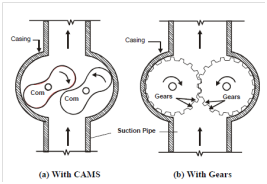
Figure : Typical Rotary Pumps
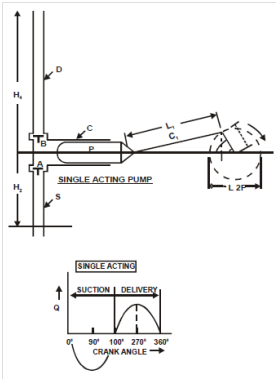
Figure : Single Acting Reciprocating Pump
Obviously the usual rotary motion of the electric motor is to be first converted into a reciprocating motion by a suitable mechanical device. Usually the speed of the electric motor is suitably brought down to the working speed of the reciprocating motion of the piston. The cylinder is linked to the suction and delivery pipes. At the beginning of both suction and delivery pipes, a non-return valve is fitted which permits the flow only from suction pipe into the cylinder, and from the cylinder within the delivery pipe. One can easily imagine that the flow rate would be pulsating (Figure) and, thus, would not be uniform unless special appurtenants are provided to even out the pulsations. Pressure rises which could be achieved, is theoretically very large and limited only by the mechanical strength of the cylinder and the pipe system. Reciprocating pump are commonly used to achieve large rise in delivery pressure heads, but the flow rates are restricted through the speeds of the piston and the discharge is associative small and uneven.