Radians:
Chapter radians will cover the measure of angles in terms of radians and degrees.
STATE the definition of a radian.
Radian Measure
The size of an angle is usually measured in degrees. Therefore, in some applications the size of an angle is measured in radians. A radian is defined in terms of the length of an arc subtended by an angle at the center of a circle. An angle whose size is one radian subtends an arc whose length equals the radius of the circle. Figure display BAC whose size is one radian. The length of arc BC equals the radius r of the circle. The size of an angle, in radians, equals the length of the arc it subtends divided by the radius.
Radians = Length of Arc/Radius
One radian equals approximately 57.3 degrees. There are exactly 2π radians in a complete revolution. Therefore 2π radians equal 360 degrees: π radians equal 180 degrees.
Although the radian is defined in terms of the length of an arc, it can be used to measure any angle. Radian measure and degree measure can be converted directly. The size of an angle in degrees is changed to radians through multiplying by π/180. The size of an angle in radians is changed to degrees by multiplying by 180/π.
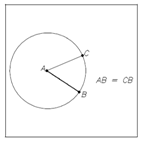
Figure: Radian Angle