Structure and function:
Triacylglycerols which is also called triglycerides or fats consist of three fatty acid chains esterified to a glycerol backbone. Easy triacylglycerols have three identical fatty acids esterified to the glycerol backbone, although mixed triacylglycerols have two or three variant fatty acid chains that is shown in figure. Triacylglycerols constitute the main fuel store and the main dietary lipid in humans. Triacylglycerols are a widely concentrated energy store. The energy acquiesce from the complete oxidation of fatty acids is about 39 kJ g-1, contrast with an energy yield of 13 kJ g-1 of carbohydrate or protein. The hydrophobic belongings of fats
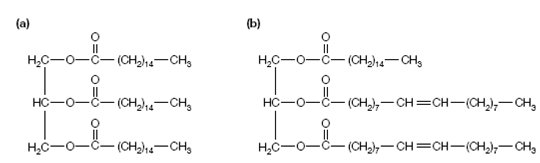
Figure: Structure of (a) a simple triacylglycerol (1,2,3-tripalmitoyl-glycerol) and (b) a mixed triacylglycerol (1-palmitoyl-2,3-dioleoyl-glycerol).
make them insoluble in water, fats are stored in specialized cells known as adipose cells (fat cells), that consist almost fully of triacylglycerol. This cell is specialized for the synthesis and storage of triacylglycerols and for their mobilization into fuel molecules. The Triacylglycerols are transported round the body in huge lipid-protein particles known as lipoproteins.