Regulation:
The breakdown of fatty acids in β-oxidation is controlled majorly through the concentration of free fatty acids in the blood that is, in turn, controlled through the hydrolysis rate of triacylglycerols in adipose tissue through hormone-sensitive triacylglycerol lipase. This enzyme is regulated through phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in response to hormonally controlled stages of the intracellular second messenger cAMP. The catabolic hormones
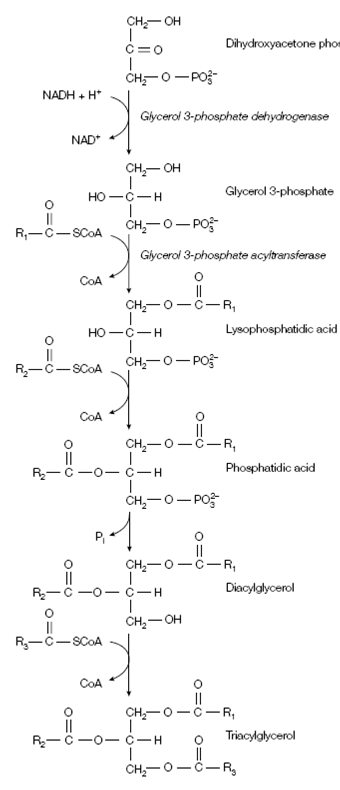
Figure: Synthesis of triacylglycerols.
Norepinephrine, glucagon, epinephrine and bind to receptor proteins on the cell surface and increase the levels of cAMP in adipose cells by activation of adenylate cyclase for features of the signal transduction path. The cAMP allosterically activates cAMP-dependent protein kinase (otherwise known as protein kinase A) which phosphorylates various intracellular enzymes including hormone-sensitive lipase. A Phosphorylation of hormone- sensitive lipase activates it, thus stimulating the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols,
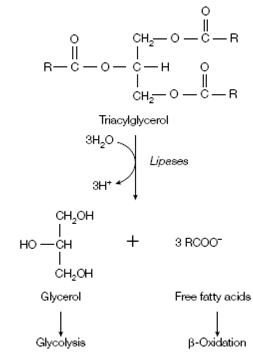
Figure: Breakdown of triacylglycerols.
raising the stages of fatty acids in the blood and subsequently activating β- oxidation in tissues like as muscle and liver. A Glucagon and epinephrine also avoid the dephosphorylation and therefore activation; of acetyl CoA carboxylase, so which fatty acid synthesis is inhibited. The anabolic hormone insulin has the opposite effect to glucagon and epinephrine. It stimulates the creation of triacylglycerols through decreasing the level of cAMP that promotes the dephosphorylation and inactivation of Hormone-sensitive lipase.
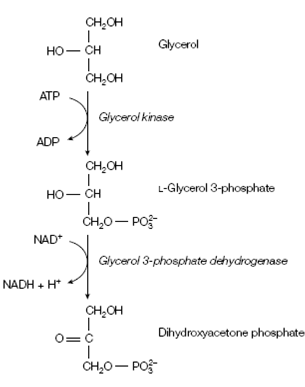
Figure: Conversion of glycerol into the glycolytic intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
Insulin also stimulates the dephosphorylation of acetyl CoA carboxylase, therefore activating fatty acid synthesis. Thereby degradation and fatty acid synthesis are coordinately controlled so as to prevent a futile cycle.
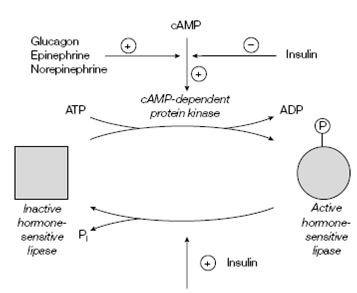
Figure: Summary of the control of hormone-sensitive triacylglycerol lipase.