States of Ionization
The successive energies needed to produce more highly charged ions, M2+, M3+ ...are the second, third,...IEs. The values all the time increase with the degree of ionization. When electrons are removed from similar shell, the main influence is that with each successive ionization there is one less electron left to repel the others. So, the magnitude of the
Change depends on the size of the orbital, because electrons in smaller orbitals are on average closer together and have more repulsion. So, with Be (2s)2 the first two IEs are 9.3 and 18.2 eV, where with Ca (4s)2 the values are 6.1 and 11.9 eV, not simply smaller to start with but with a smaller variation. The third IE of both elements is extremely higher (154 and 51 eV, correspondingly) since now the outer shell is exhausted and more tightly bound inner shells (1s and 3p, correspondingly) are being ionized. The trends are significant in understanding the stable valence states of elements.
The electron affinity of an atom may be described as the ionization energy of the negative ion, so the energy input in the process:
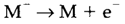
Even though, some books use a definition with the opposite sign. Electron affinities are all the time less than ionization energies due to the extra electron repulsion involved (see diagram. 1). As with successive IEs, the variation depends on the orbital size. Apparently some anomalous trends can be recognized in this way. For instance, even though the IE of F is greater than that of Cl (17.4 and 13.0 eV, correspondingly) the electron affinity of F is smaller (3.4 eV compared with 3.6 eV) partly since the smaller size of F- provides more repulsion from the added electron.
Several atoms have negative electron affinities; mean that the negative ion is not stable in the gas phase. The Second and subsequent electron affinities are always negative due to the high degree of repulsion involved in forming a multiply charged negative ion. So the O2- ion is not stable in isolation. This does not invalidate the ionic explaination of compounds like MgO, as the O2- ion is now surrounded by positive Mg2+ ions that produce a stabilizing effect (the lattice energy;).
As supposed, ion sizes decrease with increasing positive charge and negative ions are larger. Inside most ionic compounds, anions are larger than cations.