Screening
The screening of wastewater, one of the oldest treatment methods, removes gross pollutants from the waste stream to protect downstream equipment from damage, avoid interference along with plant operations and avoid objectionable floating material from entering the primary settling tanks. Screening devices might consist of parallel bars, wire mesh, rods or wires, grating, or perforated plates, to intercept large floating or suspended material. The openings might be of any shape, but are commony circular or rectangular. A material retained from the manual or mechanical cleaning of bar racks and screens is referred to as "screenings", and is either disposed of through burial or incineration, or returned within the waste flow after grinding. Principal types of screening devices are listed in Table 1 (also see Figures 1 and 2).
Table 1 : Screen Types
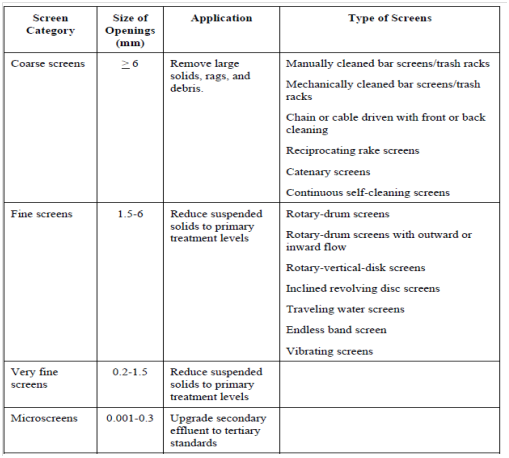
The coarse screen category includes manually or mechanically cleaned bar screens and trash racks. Bar screens consist of inclined or vertical steel bars distributed equally across a channel through which wastewater flows. That is used ahead of mechanical equipment involving raw sewage pumps, grit chambers, and basic sedimentation tanks. Trash racks and for their part, are constructed of parallel rectangular or round steel bars with clear openings. Comminutors or Regular bar screens usually follows them. Comminutors or macerators are a device that traps the material between their teeth and a fixed comb. Criteria used in the design of coarse screens involve bar size, spacing, and angle from the vertical, as well as channel width and wastewater approach velocity. Fine screens consist of several types of screen media, involving slotted perforated plates, wire mesh, woven wire cloth and wedge-shaped wire. Because of their tiny openings, fine screens have to be cleaned continuously through means of brushes, scrapers, or jets of water, steam, or air forced by the reverse side of the openings. The effectiveness of a fine screen depends on the fineness of the openings as well as the sewage flow velocity by those openings.
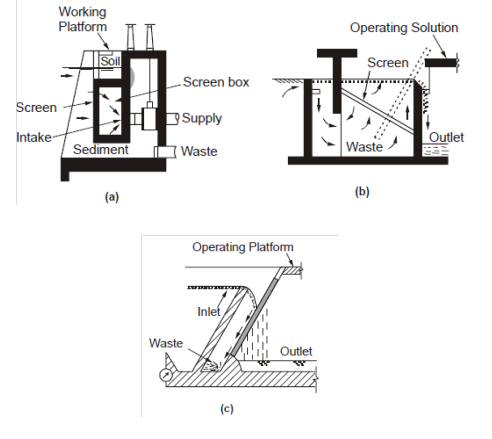
Figure 1: Manually Cleaning Fixed Bar Screens : (a) Vertical Rack Cleaned by Hand Operated Long-tined Rake; (b) Inclined Screen with Upward Flow (Screen can be tilted for cleaning); (c) Self-flushing Inclined Screen
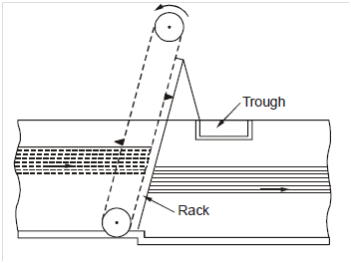
Figure 2: Mechanically Cleaned Bar Screens