Receptor-mediated endocytosis
The Receptor-mediated endocytosis is the selective uptake of macromolecules from the extracellular fiuid via clathrin-coated pits and vesicles. This procedure, that will takes place in most animal cells, included the macromolecule binding specifically to a cell surface receptor (that is an integral membrane protein). Once it is bound to the receptor, the receptor–macromolecule difficult accumulates in a clathrin-coated pit and is then endocytosed in a clathrin-coated vesicle. Receptor-mediated endocytosis gives a way of selectively concentrating particular macromolecules which are at low concentrations in the extracellular fiuid, thus raise the efficiency of their uptake without having to take in huge quantities of extracellular fiuid. One of the excellences studied and understood receptor-mediated endocytic a process is the uptake of cholesterol through mammalian cells. Several viruses and other toxins gain entry to animal cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis. While the cells do not purposely have cell surface receptors which identify the viral particle, the virus has include to express a protein on its surface which mimics the right ligand recognized through the receptor, therefore allowing the virus to bind and be internalized.
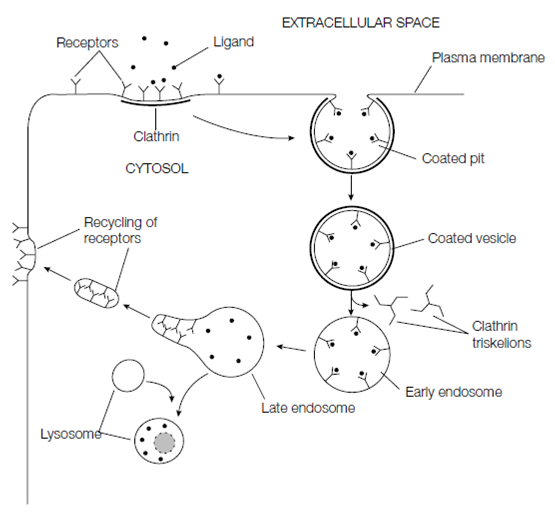
Figure: Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves clathrin-coated pits and vesicles.