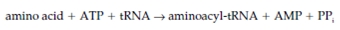Synthesis of aminoacyl-tRNA:
Every transfer RNA molecule has a cloverleaf secondary structure with the anticodon accessible at the end of the anticodon stem loop. In During synthesis of the aminoacyl-tRNA, the amino acid is covalently related to the A residue of the CCA sequence at the 3' end that was shown in the figure. Each tRNA molecule carries only a single amino acid. Moreover, since of the redundancy of the genetic code, various codons should encode the similar amino acid and so there will also exist various kinds of tRNA with corresponding anti- codons all bearing the similar amino acid. The correct nomenclature is, for instance, transfer RNAGly for the transfer RNA which will accept glycine whereas the correct
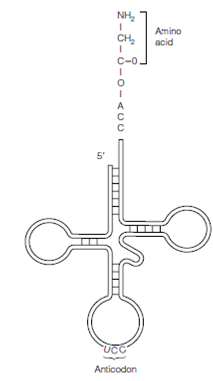
Figure: Structure of an aminoacyl-tRNA.
sponding aminoacyl-tRNA is Gly-tRNAGly, and is the aminoacyl-tRNA shown in Figure Synthesis of aminoacyl-tRNAs is crucially important for two reasons the First one is every amino acid must be covalently connected to a tRNA molecule in order to take component in protein synthesis, that depends upon the 'adaptor' function of tRNA to ensure in which the right amino acids are incorporated and the other one is, the covalent bond that is formed among the amino acid and the tRNA is a high energy bond which enables the amino acid to react with the end of the growing polypeptide chain to form a new peptide bond. For this cause, the synthesis of aminoacyl-tRNA is also referred to as amino acid activation. The Amino acids which are not connected to tRNAs cannot be added to the growing polypeptide.
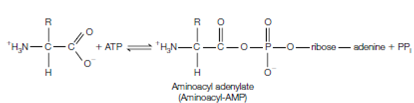
The attachment of an amino acid to a transfer RNA is catalyzed through an enzyme known as aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. The separate aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase exists for each amino acid, making 20 synthetases in total. The synthesis reaction happens in two steps. The one is the reaction of an amino acid and ATP to form an aminoacyl-adenylate that is also known as aminoacyl-AMP:
In the another step, without leaving the enzyme, the aminoacyl set of aminoacyl-AMP is transferred to the 3' end of the transfer RNA molecule to form aminoacyl-tRNA:
The whole reaction is:
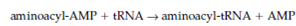
and is driven through the subsequent hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate to the inorganic phosphate.