Voltage Ratio:
The voltage of the windings in a transformer is directly proportional to the number of turns on the coils. That relationship is expressed in Equation (13-4).
VP/ VS = NP/NS (13-4)
where
VP = voltage on primary coil
VS = voltage on secondary coil
NP = number of turns on the primary coil
NS = number of turns on the secondary coil
The ratio of primary voltage to secondary voltage is called as the voltage ratio (VR). As mentioned before, the ratio of primary turns of wire to secondary turns of wire is known as the turn's ratio (TR). Through substituting into the Equation (13-4), we search in which the voltage ratio is equivalent to the turn's ratio.
VR = TR
A voltage ratio of 1:5 means in which for every volt on the primary that will be 5 volts on the secondary. A transformer is referred to as a "step-up" transformer if the secondary voltage of a transformer is greater than the primary voltage. A ratio of 5:1 means in which for each 5 volts on the primary, there will just be 1 volt on the secondary. Whenever secondary voltage is less than primary voltage, the transformer is referred as a "step-down" transformer.
Example : A transformer in above figure decrease voltage from 120 volts within the primary to 6 volts in the secondary. If the primary winding has 300 turns and the secondary has 15 turns, find out the voltage and turns ratio.
Solution:
VR = VP/VS 120/60 =20/1 =20:1
TR = NP/NS =300/15 =20/1 =20:1
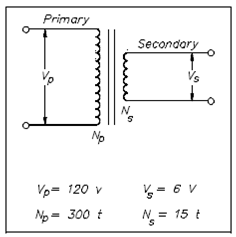
Figure:Example 1 Transformer