Initiation of transcription:
Most promoter sites for RNA polymerase II include a highly conserved sequence situated about 25-35 bp upstream for instance to the 5 side of the begin site that has the consensus TATA(A or T)A(A or T) and is known the TATA box in the another figure. Since the beginning site is indicates as position 1, the TATA box position is said to be situated at about position 25. Sequence of the TATA box resembles the 10 sequence in prokaryotes (TATAAT) except in which it is located further upstream. Both parts have essentially the similar function, namely recognition through the RNA polymerase in order to position the enzyme at the right location to initiate transcription. The sequence is around the TATA box is also important in that it influences the efficiency of initiation. Transcription is also regulated through upstream control elements that lie 5 to the TATA box that is in the below figure.
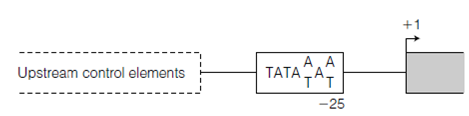
Figure: A typical promoter for RNA Pol II. The TATA box is located approximately 25 bp upstream of the transcriptional start site (denoted as 1).
Some eukaryotic protein-coding genes require a TATA box and have an initiator part instead, middle on the transcriptional initiation site. This does not have a strong consensus among genes but frequently involves a C at position 1 and an A at position 1. Till other promoters have neither a TATA box nor an initiator parts; these genes tend to be transcribed at low rates and initiate transcription somewhere within a wide region of DNA about 200 bp or so rather than at a described transcriptional beginning site.
In order to initiate transcription the RNA polymerase II needs the assistance of various other proteins or protein complexes, that are known as general (or basal) transcription factors, that must assemble into a complex on the promoter in order for RNA polymerase to bind and begin transcription that is shown in the figure. These all have the generic name of TFII for Transcription Factor for RNA polymerase II. In initiation the first event is the binding of the transcription factor IID that is also known as TFIID protein complex to the TATA box through one its subunits known as TBP TATA box binding protein. As quickly as the TFIID complex has bound, the TFIIA binds and stabilizes the TFIID-TATA box interaction. In the Next step,TFIIB binds to TFIID. Moreover, TFIIB can also bind to RNA polymerase II and so acts as a bridging protein. Therefore, RNA polymerase II that has already complexed with the TFIIF which now binds. This is followed through the binding of H and TFIIE. This final protein complex contains at least 40 polypeptides and is known as the transcription initiation complex.
Those protein-coding genes which have an initiator part instead of a TATA box appear to required another protein(s) which binds to the initiator parts. The other transcription factors then bind to form the transcription initiation complex in a same manner to which described above for genes possessing a TATA box promoter.