Tolerance Concepts
"Normal size" is the designation utilized for the purpose of general identification. Usually it is expressed in common fractions. "Basic size" is the theoretical (ideal) size from which restriction of size is specified by the application of tolerances. The basic size is the decimal equivalence of the nominal size. The number of decimal places finds out the precision or accuracy required. For instance, if the nominal width of a slot is 1¾ cm and we need accuracy to three decimal places, its basic size will becomes 1.750 cm. "Actual size" is the measured size of the finished part. "Tolerance" is the amount by which a dimension is permitted to vary. It is utilized to determine the permissible limits (maximum and minimum) of the dimension.
Tolerance may be expressed in either of two ways. A "bilateral tolerance" is indicated as plus or minus deviation from the basic size, for instance, 1.750 + 0.002 cm. A "unilateral tolerance" is a tolerance in which variation is permitted only in one direction from the basic size, for instance,
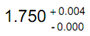
or
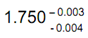
"Allowance" is the difference between the maximum material limits of mating parts, for example a shaft and a hole. It is the minimum clearance (positive allowance) or maximum interference (negative allowance) between the two mating parts.
Usually the foregoing definitions are applied by design engineers (designers) to determine the appropriate dimensions of mating features so that parts might be manufactured and might be interchangeable.