Stresses:
Let a thin seamless cylindrical shell of nominal diameter d, & shell thickness which is containing some of fluid at an internal pressure of p. The two ends of the cylinder are closed along with walls perpendicular to the shell

Figure
We will consider a vertical plane YY which cuts the cylinder anywhere along the length. We will consider the left portion of the cylinder and see the nature & magnitude of the internal stresses working on the section. The stresses shall be as illustrated in Figure.
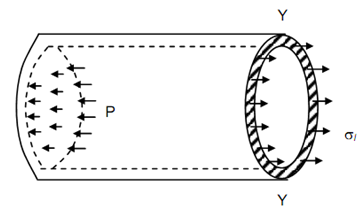
Figure
It may be seen that the internal stresses acts over the shaded annular portion of the cylinder, that is the wall area open because of the cutting the by plane Y-Y. Direction of these internal stresses shall be clearly longitudinal as the exposed areas are in the vertical plane. In addition it may also be seen that these stresses produce owing to the unbalanced horizontal force working on the left vertical wall of the cylinder, as the pressure working on the curved walls balance each other. Thus the stresses shall be tensile in nature so as to maintain equilibrium. The unbalanced force working on the left wall is called as the bursting force and the force because of internal stresses acting on the wall thickness of the cylinder is called as the resisting force.