Strains:
At any particular point in a thin cylindrical shell with an internal pressure p, we have attained the expressions for stresses along longitudinal direction and circumferential direction. In order to attain the strain along any direction, we ought to see the state of stress at any particular point. In the three mutually perpendicular directions, the stresses are as:
Stress along the radial direction = p (compressive)
Stress along with the circumferential direction = σh = pd/ 2t (tensile)
Stress along the longitudinal direction = σt = pd /4t (tensile)
The state of stress is shown in given Figure
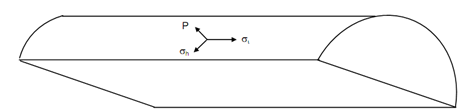
Figure
These are the principal stresses working at the point considered. Though, when d/ t is extremely large making the shell thin, the radial pressure p shall be very small compared to the longitudinal and hoop stresses. Therefore, this compressive stress may be neglected at any particular point for the purpose of working out the strain that is going to be still smaller. This assumption leaves just the two tensile stresses at any particular point, mutually perpendicular to each other. If E is refer to the Young's modulus of the material of the shell & v, its Poisson's ratio, after that the expression for the strains in the two direction are attained as follows :
Longitudinal strain εl = σ l / E - v σ n/ E
= (pd/4tE ) - v ( pd/2t E)
= (pd /4tE) (1 - 2v)