Q: Calculate the value of voltage Vo from Thevenin's theorem.
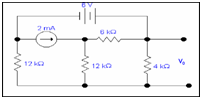
Solution:
We have to calculate V0 by using Thevenin's theorem .
Step 1: Remove RL
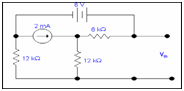
In the circuit value of RL is equal to 4k resistor at which we have to calculate the voltage Vo.
Step 2: Calculating the value of Vth
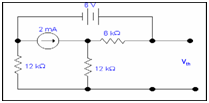
We have to calculate Vth .By applying KVL in two loops to compute the individual loop currents.
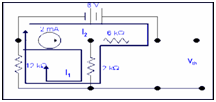
Here, I1 = 2mA
By applying KVL for the super mesh
-6 +6kI2 +12k (I1 +I2) +12k (I1 +I2) =0
-6 +6kI2 +12kI2 +24kI1 + 12kI2 =0
30kI2 - 6 +24k (2m) =0
30KI2 -6 +48 =0
I2 = -42/30mA
I2= -1.4mA
Now calculate the voltage around 6k & 12 k to estimate the value of Vth
So V6k = 6kI2
= 6k(-1.4m) //putting the value of I2
V6k = -8.4V
V12k = 12k (I1 +I2)
= 12k( 2m -1.4m) =7.2V
Therefore,
Vth = V6k + V12k
= -8.4 +7.2 = -1.2V
Step 3: Determining value of Rth
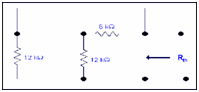
6k is in series to 12k .The resultant of these will be in parallel with 12k.
So, (6k+12k) ||12k = 18k x12k/ (12k+18k)
Rth = 7.2k
Step 4: Determining the unknown quantity.
After computing Vth & Rth, re-inserting the load resistance RL in the circuit in series along Rth and supposing the Vth like a battery in series along these two resistances.
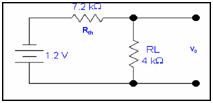
V0 = -1.2 x4k/(7.2k + 4k)
V0 = - 0 .4285V