Q: Determine the voltage Vo by using Thevenin's theorem.
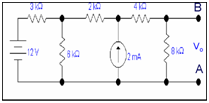
Solution:
We have to calculate V0 by utilizing Thevenin's theorem .
Step 1: Remove RL
Here value of RL is 8k resistor at which we desire to calculate the voltage Vo.
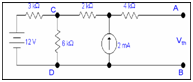
Step 2: Finding the value of Vth
To calculate Vth we will use superposition method
When only voltage source is active
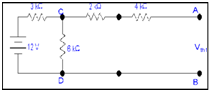
No current will pass in 'CA' branch therefore voltage drop across 4k & 2k resistor is zero therefore
VCD = Vth1
Now by voltage division rule
VCD =Vth1 =V6k = (12 x6)/(3+6)
= 8 V
Now when only current source is active
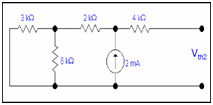
3k||6k = (3k x6k)/(3k+6k)
=2k
2k is in series to 2k =4k
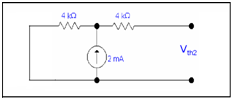
Current flow through open circuit is zero by using ohm's law so
Vth2 = 4k x2m
Vth2= 8 V
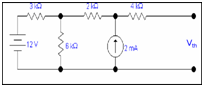
Therefore
Vth = Vth1 +Vth2
= 8 +8 = 16 V
Step 3: Determining Rth
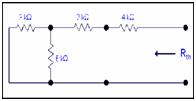
3k||6k = (3k x6k)/9k= 2k
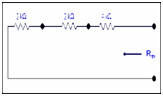
Rth = 2k+2k+4k =8k
Step 4: Determining unknown quantity.
After determining Vth & Rth, re-inserting the load resistance RL in the circuit in series along Rth and letting the Vth like a battery in series along these two resistances.
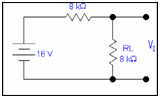
V0 = (8k/16k) x16
V0= 8 V