Hooke law:
Hence,
γ r = r . Δ θ/ Δ l
However γr remains constant for any given value of r, hence, Δ θ /Δ l should also be a constant. This means that the ratio of angle of twist and length of shaft is a constant, that means and θ / l is constant
Δθ / Δ l = θ/ l
Hence,
γr = r . θ/ l
Since Hooke's law is followed γr = τr /G
where τr is the shearing stress at any point on a circle of radius r as γr is the shearing strain at the same point. G is modulus of rigidity of the shaft material. Using this value of γr in Eq. and obtaining
τr / r = Gθ / l
The right hand side of Eq. is a constant for a given length of shaft under a given torque T. Thus, this equation states that ratio of stress at a point to radial distance of that point from the centre of the cross-section is constant. If the shearing stress at any particular point is d/2 called τm, the radial distance of that point from the centre of the cross-section shall be and hence,
τr / r = τm/(d/2) = Gθ /l
or, τm = Gθ/ l
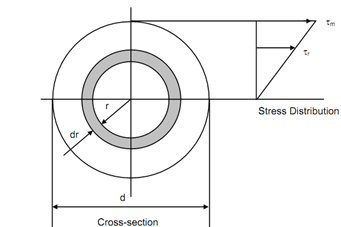
Apparently the distribution of shearing stress is given by the equation τr = r (Gθ/l) which shows τr is uniformly distributed with radius r. The values of τr = 0 at r = 0, i.e. at centre and the shearing stress will be maximum while r = d , i.e. on the surface of the shaft.
Thus, τm is the highest value of stress caused by torque T. The distribution of shearing stress over shaft cross-section is shown in Figure.
Figure