Retaining Walls:
While a mass of material, whether it is liquid or granular solid, is required to be maintained at a higher level on only one side, the dividing structure between the two is known as a 'retaining wall' when a solid is retained, or a 'dam' when a liquid is retained.
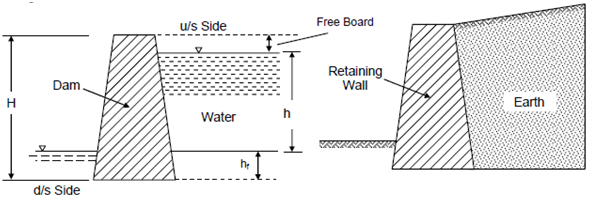
(a) (b)
Figure
In Figure (a), water at a higher level, since within a reservoir, etc., is maintained at a height 'h' on the right hand (up-stream) side of the dam. In Figure (b) earth on the right hand side is retained at a level higher than on the left hand (down-stream) side, and it is managed so through the wall. In either case the dam or wall acts as a retaining wall which prevents the material (liquid or granular solid) from slipping or flowing towards the left; and, therefore, it is under a horizontal pressure which tends to overturn it or move it towards the left. The retaining wall should be good enough to prevent any such event or fail under such a pressure. The weight of the wall and the horizontal pressure exerts pressure on the soil below foundation which should also be within safe limits.