Magnetic Moment
Any nucleus with a spin angular momentum quantum number, I ≠ 0, that corresponds to a spinning positive charge and you know that any spinning charge will generate a magnetic moment (µ). The magnetic moment, µ, of a spinning nucleus is proportional to its spin angular momentum (I) and is given by the following expression.
µ = ( gNe/2m)I
where, gN is called the nuclear g-factor which is characteristic of the particular nucleus (for proton its value is 5.585), e is a charge on a proton and m is the mass of the proton. The magnetic moment vector is in the similar direction as the angular momentum vector.
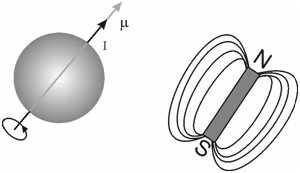
Figure: Spin angular momentum or the magnetic moment having the same direction
We can get the relationship among the magnitude of magnetic moment and spin angular momentum quantum number by substituting the value of the magnitude of spin angular momentum in from as given below.
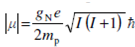
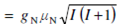
where µN =e h/2 mp and is called the nuclear Bohr magneton.