Larmor Precession:
In order to understand the phenomenon of Larmor precession, you need to recall the behaviour of a spinning top (or a gyroscope). You would recall that the spinning top executes two concurrent motions. It spins on its axis as well as around its axis. The motion around the vertical axis arises due to the interaction of spin, i.e., gyroscopic motion with the earth's gravity acting vertically downward. This motion is called precessional motion and the spinning top is said to be precessing around the vertical axis of the earth's gravitational field as depicted in Figure. You should also remember that only a spinning top undergoes precessional motion whereas static top does not do so.
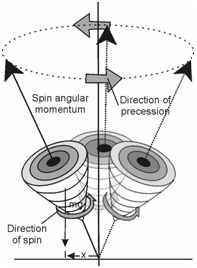
Figure: Precessional motion of a spinning top due to earth's gravitational field
A spinning nucleus (or proton) when placed in an external magnetic field also exhibits precessional motion. A spinning nucleus within the presence of an external magnetic field can process around the axis of an external magnetic field in two ways; it can either align with the field (low energy state) or it can oppose the field direction (high energy state) as typically illustrated in Figure where B0 is the external magnetic field. ?E represents the energy of the transition between two orientations.