Cost Push Inflation or supply Inflation:
It is a situation where the process of increasing price level is caused by increasing costs of production which push up prices.
Cost push inflation is also referred to as supply inflation. Price level in this case increases due to an increase in business costs e.g. wage increase, high interest rates, etc. These increases in prices occur in the face of high unemployment and slacken resource utilization. The increase in cost of production causes supply of final goods and services to fall. This creates excess aggregate demand and a new equilibrium is attained at a higher price level.
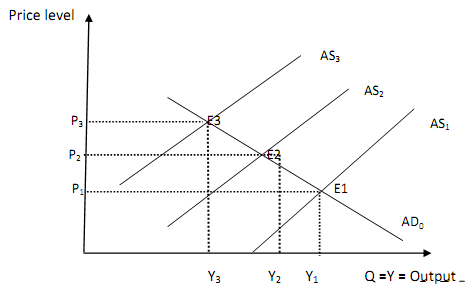
Figure illustrates the process of cost push inflation. The aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves interest at point 'E1' and the general price level is p1 and output is at Y1. Assuming there is an increase in cost of production via increased wages throughout the economy, the aggregate supply curve will shift upward from As1 to As2. The general price level will increase and output will fall from Y1 to Y2. If this process continues it leads to another round of increase in cost of production. Aggregate supply falls from AS2 to AS3 and the general price level, rises from P2 to P3. Output will fall again to Y3.