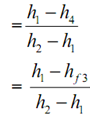Vaporizing Process:
The liquid-vapour mixture of the refrigerant at temperature T4 = T1 and pressure p4 = p1 is evaporated and modified into vapour refrigerant at steady pressure & temperature, as indicated by the horizontal line 4-1 on T-s & p-h diagrams. Throughout evaporation, the liquid-vapour refrigerant absorbs its latent heat of vaporization from the medium (air, water or brine) which, is to be cooled, this heat that is absorbed by the refrigerant is known refrigerating effect and it is in brief written like RE. The procedure of vaporization continues up to point 1 that is the beginning point and therefore the cycle is finished.
We know that the heat absorbed or refrigerating effect or extracted by the liquid-vapour refrigerant throughout evaporation per kg of refrigerant is given by
RE = h1 - h4 = h1 - hf3
Here hf3 = Sensible heat at temperature T3, that means enthalpy of liquid refrigerant leaving the condenser.
This can be noticed from the cycle that the liquid-vapour refrigerant has extracted heat throughout evaporation and the work shall be done through the compressor for isentropic compression of the high temperature & pressure vapour refrigerant.
Coefficient of performance, C.O.P. = (Refrigerating effect)/( Work done)