Fahrenheit Scale:
In most of the English-speaking world, and particularly in the United States, the Fahrenheit temperature scale (°F) is used by laypeople. A Fahrenheit degree is of the same size as a Rankine degree. Though, the scale is located differently. The melting temperature of pure water ice at sea level is +32°F, and the boiling point of pure liquid water is +212°F.Therefore, +32°F corresponds to 0°C, and +212°F corresponds to 100°C.The Absolute zero is around -459.67°F.
The most general temperature conversions you are likely to perform include changing a Fahrenheit reading to Celsius, or vice-versa. The formulas have been developed for this aim. Assume F be the temperature in °F, and assume C be the temperature in °C. Then, if you require converting from °F to °C, use the formula shown below:
F = 1.8C + 32
If you require converting a reading from °C to °F, use this formula:
C = 5/9(F - 32)
While the constants in such equations are expressed only to one or two significant figures (1.8, 5/9, and 32), they can consider mathematically correct for computation purposes.
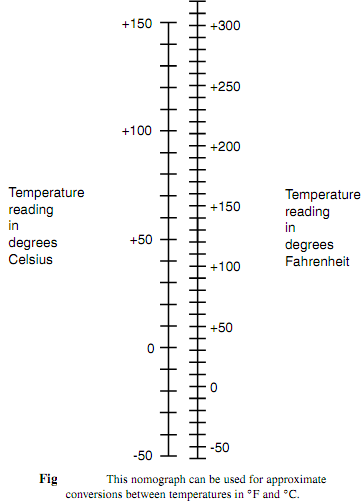
Figure shown below is a nomograph you can use for estimated temperature conversions in the range from -50°C to +150°C.
Whenever you hear someone say that the temperature at the core of a star is 30 million °F, the Rankine reading is around the same, but the Celsius and Kelvin readings are only around 5/9 as great.
PROBLEM:
Determine the Celsius equivalent of a temperature of 72°F?
SOLUTION:
To resolve this, simply use the conversion formula for converting Fahrenheit temperatures to Celsius temperatures:
C = 5/9(F - 32)
Therefore, in this situation:
C = 5/9(72 - 32)
= 5 /9 x 40 = 22.22°C
We are defensible in carrying this out to only two significant figures as this is the extent of the accuracy of our input data. Therefore we can conclude that the Celsius is equal to 22°C.