Modes Of Heat Transfer
(A) Conduction:
The easiest form of communication is by contact among the systems, either straightforwardly or across a separating layer. The heat interaction which takes place now is known as the heat conduction. The rate (W/m2) of heat conduction is relative to the prevailing temperature gradient (K/m), and is specified by the Fourier’s law:
q = - kA Δ T
Here the proportionality constant k is known as the thermal conductivity (W/m.K). It is a material property, usually large for metals, smaller for non-metallic solids & liquids, and smallest for gases.
(B) Convection:
When the conducting medium is a fluid in motion, the mode of heat transfer termed as the convection. The method of the convection might be described with reference to a (double pipe) heat exchanger in which a flowing fluid is restricted among a hot and a cold surface. The heat transfer from the hot surface to the fluid particles in contact with it takes place by conduction; causing the fluid temperature to increase. The warmed fluid, being in motion, consequently comes into contact with the cold surface that is lower in temperature than the fluid, and heat transfer takes place by conduction from the fluid to the cold surface.
There are two kinds of convection:
(a) Forced convection.
(b) Free convection.
In forced convection, as explained above, the fluid motion is “forced” by an exterior agency, like a compressor or pump. In free or natural convection, the fluid motion occurs as an outcome of density differences caused by the temperature differences. The convection currents that might be discerned in the water contained in a vessel heated from below, or the vertical motion of hot gases in candle flame, are illustrations of free convection.
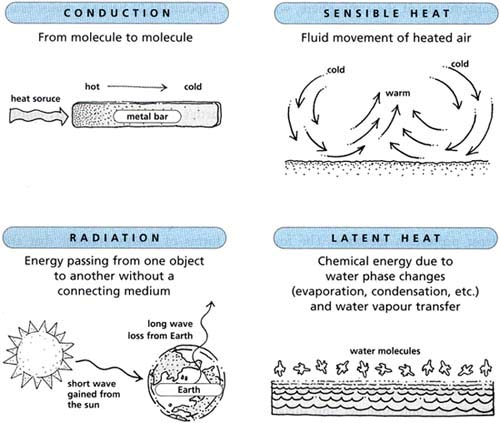
(C) Radiation:
Even whenever the intervening space among two systems has no matter or material, the systems are yet in thermal communication. The electromagnetic radiation is transferred among the surfaces, and it does not need any material communication. The radiative transfer from the sun to the earth is a well-known illustration. The rate of radiative heat transfer is much more responsive to the temperatures of the surface than the rates of conduction and convection. It is frequently negligibly small at room temperature.