Aerated Lagoons
An aerated lagoon is a basin between 1 and 4 metres in depth in which wastewater is treated either on a flow-through basis or with solids recycling. The microbiology included within this process is same to in which of the activated-sludge procedure. Therefore, differences arise since the large surface area of a lagoon might cause more temperature effects than are ordinarily encountered in conventional activated-sludge processes. Wastewater is oxygenated through surface, turbine or diffused aeration. The turbulence created through aeration is used to keep the contents of the basin within suspension. Depending on the retention time, aerated lagoon effluent holds approximately one third to one half the incoming BOD value in the form of cellular mass. Most of these solids must be erased in a settling basin before last effluent discharges (Figure 17).
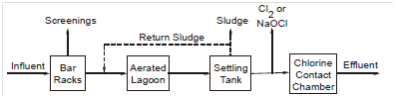
Figure 17: Typical Flow Diagram for Aerated Lagoons