Information Engineering: An Overview
The target of information engineering IE is to describe architecture which will enable a business to use information efficiently. In addition information engineering works to create an overall plan for implementing that architecture {SPE93}. There are 3 architecture that must be designed and analyzed within the context of business goal and objective that are as given below:
- Data architecture
- Application architecture
- Technology infrastructure
The data architecture offers a framework for the information requirement of a business function or business. The individual building blocks of the architecture are the data objects which are used through the business. The data objects flow among business functions are organized within a database and are transformed to give information which serves the requirement of the business.
Application architecture encompasses those elements of a system which transform objects within the data architecture for some business purpose. In the circumstance of this book we normally consider the application architecture to be the system of programs which performs this transformation. Moreover in a broader circumstance, the application architecture might incorporate the role of business procedures and people which have not been automated.
The technology infrastructure gives the foundation for the application architectures and data. The infrastructure encompasses the software and hardware which are used to data and support application. Which includes computers and telecommunication links, computer networks, storage technologies and the architecture which has been designed to implement these technologies?
The model the system architectures offered earlier a hierarchy of information engineering activities is described. The figure 12.3 is describe the world view is achieved by information strategy planning (ISP) ISP views the fully business as an isolates and entity the domains of the business which are important to the overall enterprise. ISP describes the data objects which are visible at the enterprise level, their relationships and how they flow among the business domains.
The domain view is addressed with an IE activity called business area analysis (BAA). Hares [HAR93] define (BAA) in the following manner:
BAA is concerned with identifying in detail function and data needs of selected business field identified during ascertaining and ISP their interactions. It is only concerned with specifying what is needed in a business field.
As the information engineer starts BAA the focus narrows to an exact business domain. BAA views the business field as an isolates and entity the business functions and process which enable the business fields to meet its target and objective. BAA such as ISP describes data objects their relationship and how data flow. But at this stage these characteristic are all bounded through the business area being analyzed. The outcome of NAA is to isolate fields of opportunity in that information systems may support the business fields.
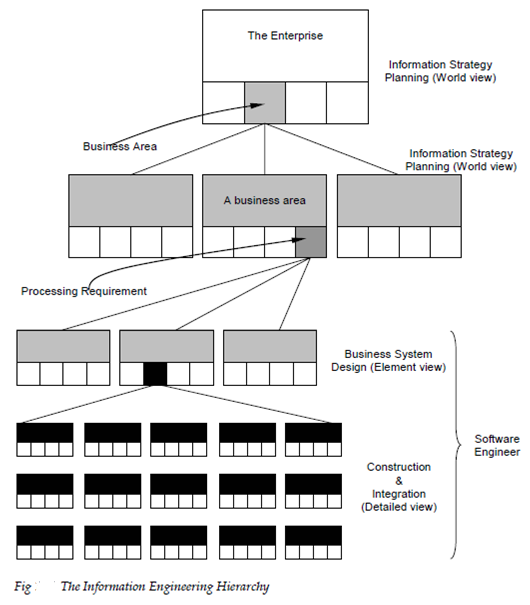
Once an information system has been isolated for future development IE makes a change into software engineering. Through invoking a business system design step the basic needs of a specific information system are modelled and these requirement are translated into applications architecture, data architecture and technology infrastructure.
The final IE step integration and construction (I&C) focuses on implementation detail. The infrastructure and architecture are implemented through constructing an internal data and appropriate database structures through building application using program elements and through selecting appropriate component of a technology infrastructure to support the design build during BSD. Each of these system elements must then be included to form a complete information system into the business field circumstance performing all user logistics and training support to achieve a smooth transition.