Helical Sweep Surface:
Complex paths may be developed by combining simple paths. For instance, combining the two earlier path transformations yields a single turn of a helical path along the z-axis, that is
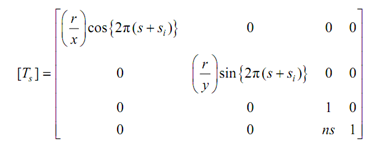
The simplest sweep surface is attained by traversing a line segment along with a path. Recalling that the parametric equation of a line segment is
P (u) = P1 + (P2 - P1) u 0 ≤ u ≤ 1
The corresponding sweep surface is specified by
Q (u, s) = P (u) [T (s)] 0 ≤ t ≤ 1, s1 < s < s2
Here again [Ts] is the sweep transformation. If the sweep transformation have only translations and/or local or overall scaling, the resulting surface is planar. If the sweep transformation has rotations, the resulting surface is non-planar. Figure illustrated the helical sweep surface attained by simultaneously translating along and rotating around the x-axis a line originally parallel to the y-axis. An instance more fully explains the technique.
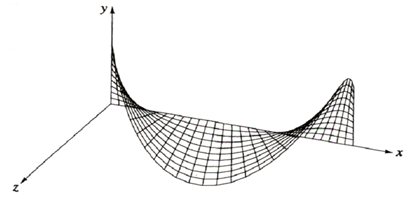
Figure: A Helical Sweep Surface
Parametric curves, for example., cubic splines, parabolically blended, Bezier & B-spline curves, are also utilized to generate sweep surfaces. Figure illustrated a sweep surface generated from a single cubic spline curve segment swept parallel to the z-axis.