Non-linear Sweep:
In non-linear sweep, the path is a curve distinct by a higher-order equation (quadratic, cubic or higher) as illustrated in Figure (b).
Hybrid Sweep:
This combines linear and/or non-linear sweep via set operations. Figure (a) illustrated the same object illustrated in Figure (a) but with a hole. In this case, two point sets are swept in two different directions and the two resulting swept volumes are glued together to form the ultimate object. Invalid solids or non-regular sets can result if the sweeping direction is not chosen properly as illustrated in Figure (b).
In engineering applications Sweeping operations are useful that includes swept volumes in space. Two extensively known applications are simulations of material elimination due to machining operations and interference detection of moving objects in space.
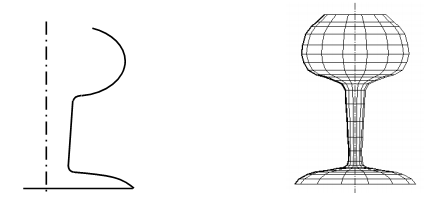
Figure: Linear, Non-linear and Invalid Sweeps
Sweep representation is useful once it produced. Its modelling domain may be extended beyond 2½ - D objects if non-linear sweep is available. Non-linear sweep can be useful in making non-rigid objects and learning their deformations they travel in space. Complicated mechanical parts such like screws, springs, and other components that need helical and special loci may be represented by sweeping.