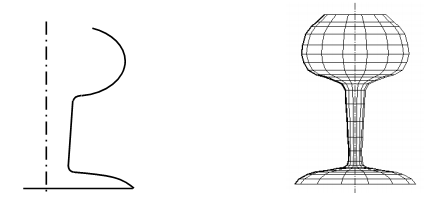
Linear Sweep:
In linear sweep, the path is a linear or circular vector explained by a linear, most frequently parametric. Linear sweep may be divided into translational and rotational sweep. In translational sweep, planar two-dimensional point set explained through its boundary (or contour) may be moved a given distance in space in a perpendicular direction (called the directrix) to the plane of the set (Figure (a)). For rotational sweep, the planar two-dimensional point set is rotated around the axis of rotation by a given angle (Figure (a)).