Basic Concepts:
There are two kinds of surfaces - parametric & implicit - that are commonly uytilized in modelling systems. Parametric surfaces are explained by a set of three functions, one for each coordinate, as:
p (u, v) = (x (u, v), y (u, v), z (u, v))
where parameters u and v are in certain domain. For our reason, we will assume both u and v are in the range of 0 and 1. Therefore, (u, v) is a point in the square explained by (0, 0), (1,0), (0, 1) and (1, 1) in the uv-coordinate plane. Figure show this concept.
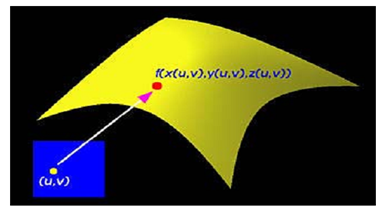
Figure: Parametric Model of Surface
Implicit surfaces, alternatively, are defined by a polynomial of three variables:
p (x, y, z) = 0
Alike to curves, if x (u, v), y (u, v) and z (u, v) are polynomials, parametric surfaces shall not be able to represent several surfaces that are normally explained by implicit surfaces. The sphere is a good instance. You may easily prove this fact with an argument alike to that utilized for circles. If x (u, v), y (u, v) and z (u, v) are rational polynomials (that is quotients of two polynomials), parametric surfaces may represent spheres, ellipsoids and many other surfaces. Though, similar to curves, several implicit surfaces do not have any parametric form. Thus, in terms of expressive power, implicit surfaces are more powerful than parametric surfaces.