Principle of NAA:
The technique of NAA involves two steps; irradiation of a sample with neutrons and subsequent measurement of the induced radioactivity. The radionuclides are characterized by their characteristic γ-ray energy and half-life as illustrated in Figure.
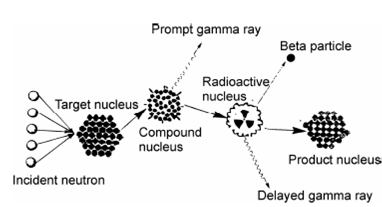
Figure: Basic principle of Neutron Activation Analysis
In this process, the rate of formation of the product atoms (Np) is represented as;
dNp/dt = N σ φ - λ Np = N σ φ - λ N1
here N is the number of the target atoms of an element in the sample [ iw NA /M]
i denotes the isotopic abundance; w is the concentration of element; M is the mass of the target atom; NA is the Avogadro number;
σ denotes the thermal neutron absorption cross section in barns (b = 10-24 cm2);
φ is the neutron flux (n cm-2 s-1), and
λ is the decay constant (s-1) = (0.693/ t1 / 2) and t1/2 = half life of the product nucleus.
On integration, Eq. (13.6) yields
λ N1 = A = N σ φ (1 - e- λti )
where ti is the irradiation time. Since the sample is delayed for time td before counting using a counter along with effectiveness ε, and gamma-ray abundance γ, the complete equation can be written as;
A = ( wiNA/M) σ φ (1 - e - λti ) e - λtd ε γ =(wiNA/M) σ φ S D C ε γ
where S = (1 - e - λti ) is saturation factor, D = (e - λtd ) is delay factor, and
C = (1 - e - λt c )/ λ is the correction factor for decay during counting time tc.