Neutron Sources:
A wide range of devices is used to produce neutrons needed for activation analysis. Some are sophisticated and extremely expensive, while others are rather simple and modest in cost. In Table 13.1 are listed some commonly used neutron sources. These may be classified into three groups: isotopic and machine type sources and nuclear reactors. As evident from Table, isotopic neutron sources are characterized by low flux, mobile and have low cost. These are good for
Table : Common Sources of Neutrons for NAA
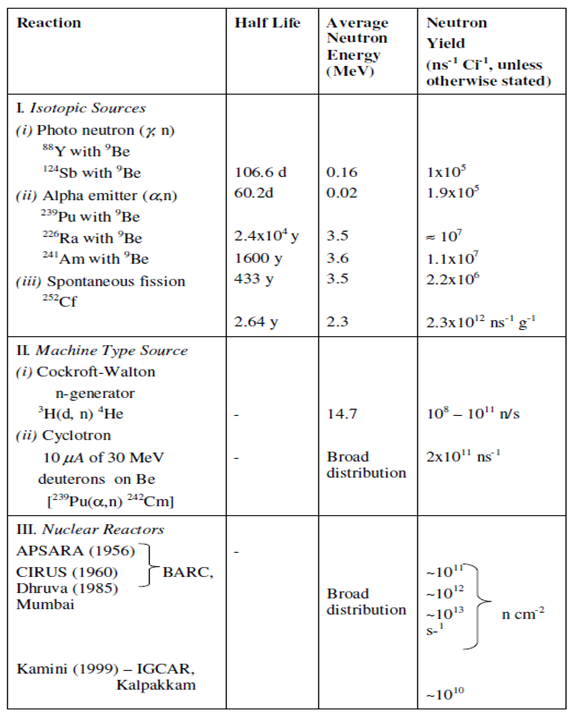
demonstration experiments and for the determination of main constituent elements such as Al, Mn and Cu in bauxite, pyrolusite and pyrite respectively. Therefore, these have limited life and are not good for trace element analysis. On the other hand machine categories sources have the advantage of being put off when not in use. On the other hand reactor neutrons are most widely used for NAA work. These have wide energy spectrum as described in Figure. Neutrons may be classified on the basis of energy viz. thermal (0.025 eV), epithermal (1 eV-1 keV) and fast (>1MeV). Several activation methodologies have been developed depending on the energy of neutrons. A brief description of these methodologies is defined here.
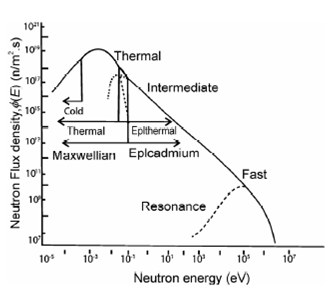
Figure: Neutron energy spectrum in a nuclear reactor