Structure and properties:
A fatty acid consists of a hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxylic acid group that is shown in the figure. Most fatty acids found in biology have an even number of carbon atoms arranged in an unbranched chain. Chain length commonly ranges from 14 to 24 carbon atoms with the most general fatty acids containing 16 or 18 carbon atoms. The saturated fatty acid has all of the carbon atoms in its chain saturated with hydrogen atoms. This provides the common formula CH3 (CH2)nCOOH, where n is an even number. The Monounsaturated fatty acids have one double bond in their structure although polyunsaturated
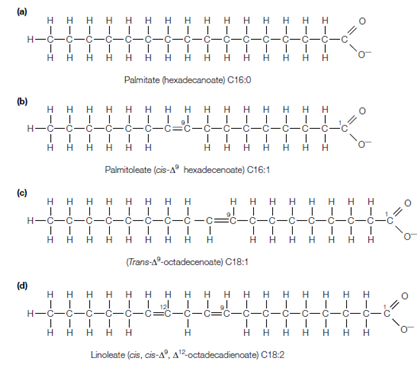
Figure: Structures of (a) a saturated fatty acid (palmitate, C16:0); (b) a monounsaturated fatty acid with the double bond in the cis configuration (palmitoleate, C16:1); (c) a monounsaturated fatty acid with the double bond in the trans configuration (C18:1); and (d) a polyunsaturated fatty acid (linoleate, C18:2).
fatty acids have two or more double bonds shown in the figure. The twice bonds in polyunsaturated fatty acids are separated through at least one methylene group.
The characteristics of fatty acids depend on their chain length and the number of double bonds. The Shorter chain length fatty acids have lower melting temperatures than those with longer chains. Unsaturated fatty acids have minor melting temperatures than saturated fatty acids of the same chain length and whilst the corresponding polyunsaturated fatty acids have even lower melting temperatures.