Prostaglandins:
Prostaglandins and the structurally associated molecules prostacyclins, leukotrienes and thromboxanes, are known as eicosanoids because they contain 20 carbon atoms. These hormones are associativaly short-lived and therefore act locally near to their site of synthesis in the body. They are derived from the general precursor arachidonate described in the figure. This polyunsaturated fatty acid is a derivative of linoleate show in Table 1. The Prostaglandins kindle inflammation, modulate synaptic transmission among nerve cells, and induce sleep. While aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) has been used for centuries to decrease inflammation, fever and pain, it was not until year of 1974 which John Vane discovered how aspirin works. Aspirin hold back the synthesis of prostaglandins through irreversibly inhibiting prostaglandin synthase. This enzyme catalyzes the first phase in the synthesis of prostacyclins and thromboxanes, prostaglandins.
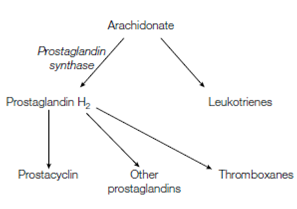
Figure: Biosynthetic relationship of the eicosanoids.