Covalent Bonding and Hybridization
A covalent bond binds two atoms jointly in a molecular structure and is created while atomic orbitals overlap to make a molecular orbital - so called since the orbital belongs to the molecule like a whole rather than to one particular atom. A simple instance is the creation of a hydrogen molecule (H2) from two hydrogen atoms. Every hydrogen atom has a half-?lled 1s atomic orbital and while the atoms approach each other, the atomic orbitals interact to make two MOs (the number of resulting MOs has to be equal the number of original atomic orbitals, diagram).
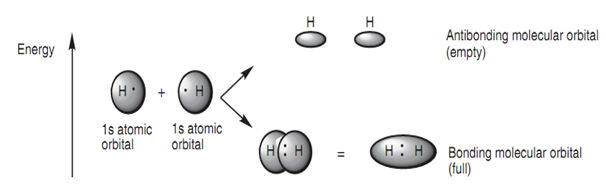
Diagram: Molecular orbitals for hydrogen (H2).