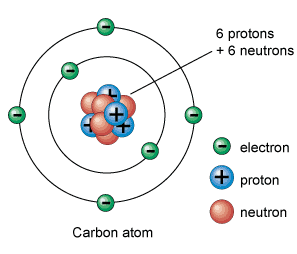
Atomic Structure of Carbon:
Carbon (from Latin: carbo "coal") is the chemical element represented by the symbol C and atomic number 6. Since a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent- creating four electrons available to create covalent chemical bonds. There are 3 naturally occurring isotopes, along with 12C and 13C being stable, when 14C is radioactive, decaying with a half-life of about 5,730 years. Carbon is one of the some elements known because of antiquity.
There are various allotropes of carbon of which the best known are diamond, graphite, and amorphous carbon. The physical properties of carbon change extensively with the allotropic form. For instance, diamond is highly transparent, whereas graphite is opaque and black. Diamond is the most hard naturally-occurring material known, whereas graphite is soft sufficient to create a streak on paper (therefore its name, from the Greek word "to write"). Diamond has a very low electrical conductivity, where as graphite is a very good conductor. Under standard circumstances, diamond, carbon nanotube and graphene have the highest thermal conductivities of all known materials.